Purpose: The aim of the study was to evaluate ocular surface and tear film in patients with pediatric (primary or secondary) unilateral glaucoma and compare results obtained from the treated eye and untreated healthy eye.
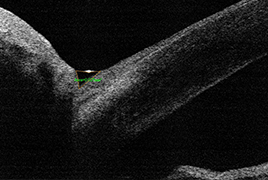
Methods: Patients with unilateral pediatric glaucoma, followed in the outpatient department of the Department of Ophthalmology, Motol University Hospital, were included in this study. Tear osmolarity, corneal epithelial thickness, lower tear meniscus area, Schirmer test, corneal fluorescein staining and tear break-up time test (TBUT) were evaluated in both healthy and treated eye. The Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) was used to establish subjective impairment. The values obtained through testing the healthy and treated eye were compared.
Results: Thirteen patients met the inclusion criteria of the study. The mean age of the patients was 17.2 ± 8.1 years. There was statistically significant decrease in corneal epithelial thickness and TBUT in the treated eye (45.9 ± 5.3 µm, 6.0 ± 1.7 second resp.) compared to the healthy eye (50.2 ± 2.6 µm, 8.8 ± 3.2 second resp.; p = 0.0106, p = 0.0015 resp.). Fluorescein staining score of the ocular surface was higher in the treated eye (1.7 ± 2.1) than in the healthy eye (0.5 ± 0.8; p = 0.0243). We found no statistically significant difference in the other evaluated parameters between the treated and the healthy eyes.
Conclusion: The results confirmed signs of ocular surface damage in treated eyes. The damage may be induced by chronic topical antiglaucoma therapy, but that could be a consequence of the previous ocular surgery as well. The possible damage of the ocular surface should be taken into account when selecting appropriate treatment in these patients.