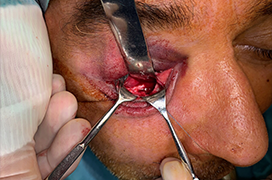
Aims: The aim of this study is to retrospectively evaluate the use of a transconjunctival surgical approach in maxillofacial surgery on the fractures of the infraorbital rim and the orbital floor by analyzing the operating time, the incidence of perioperative and postoperative complications, as well as the functional and aesthetic outcomes of transconjunctival surgical treatment.
Materials and methods: All the patients on whom we used a transconjunctival approach from December 2017 to December 2021 were included in this retrospective study. The epidemiological causes of fractures of the midface skeleton were analyzed. The length of the operating time of the transconjunctival approach with lateral canthotomy was compared with a control group in which the supraorbital eyebrow approach was performed. In addition, we analyzed the incidence of perioperative and postoperative complications in comparison with publications from other centers.
Results: We used the transconjunctival approach 103 times on 89 patients (in 14 patients the transconjunctival approach was performed bilaterally). In cases where the lateral canthotomy was used to extend the transconjunctival approach, there was no prolongation of the operating time. Perioperative complications included the perforation of the lower eyelid in 2 patients. In the postoperative period we recorded complications in 3 patients. Ectropion of the lower eyelid was present in one patient and entropion of the lower eyelid was observed in two patients. The percentage of perioperative and postoperative complications does not exceed the incidence of complications in transcutaneous approaches on the infraorbital rim.
Conclusion: Based on the results of our study, we can consider the transconjunctival approach, either alone or in combination with lateral canthotomy, to be a safe surgical technique, associated with a low risk of complications. Thanks to mucosal incision of the conjunctiva of the lower eyelid, it completely eliminates skin scarring on the face. Our results are comparable with the published results of foreign authors and workplaces with larger cohorts of patients, which similarly evaluate the transconjunctival approach as a quick and safe surgical approach to the inferior orbital rim, with a low risk of complications.