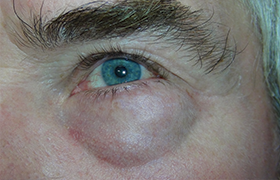
Chronic eyelid edema may be a symptom of different disease. The most common are autoimmune diseases such as orbital pseudotumor, vasculitis, sarcoidosis, or impaired vascular or lymphatic drainage. Rarely has it been reported as the sole manifestation of the lymphoma. Eyelid lymphoma is a special clinical entity in the spectrum of hematological malignancies. Here we present our clinical experience with eyelids lymphomas. First case is a 76-year-old female patient with bilateral edema of upper eyelid non-responding to anti-inflammatory therapy. Histological examination diagnosed mantle cells lymphoma. In the second case, 58-year-old patient was diagnosed with solitary unilateral tumor of the lower eyelid, where primary biopsy was ordered and diagnosis of MALT lymphoma was established after histological examination. In both cases, it was not solitary eyelid tumor, but systemic disease with multiple lymphadenopathy and bone marrow infiltration were found in follow-up examinations. Subsequently, patients care was given to the hemato-oncologist.
- Innovative Strategies for Treating Retinal Diseases
- Assessment of the Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy in Patients with Chronic Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
- Sensitivity and Specificity in Methods for Examination of Ocular Astigmatism
- Evaluation of Retinal Light Scattering, Visual Acuity, Refraction and Subjective Satisfaction in Patients after Acrysof IQ Panoptix Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Eyelid Edema as a First Sign of Lymphoma
- Ocular Symptoms of Rosacea