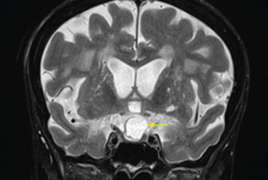
A seventysix-year-old female was acutely admitted to the Eye Clinic of the University Hospital in Martin with a 1 month history of impaired central and peripheral vision on the right eye. At the admission patient`s right eye VA was fingers at 20 cm, the left eye had a central vision preserved. Magnetic resonance of the brain and orbits demonstrated cystic tumor expansion in the sellar region with compression of optic chiasm and optic nerves (more on the right side), in diff. dg. as cystic macroadenoma of the pituitary gland. Endocrinological examination found secondary hyperprolactinaemia from pituitary oppression, other hormonal parameters were without deviation. Consequently, the ENT examination recommended endoscopic resection via the transsphenoid approach. After resection of the lesion and histological examination of the sample, the finding was evaluated as a Rathke’s cleft cyst. Symptomatic Rathke's cleft cysts of pituitary gland are rare, but the visual symptoms are typical findings due to chiasm proximity. On ophthalmological examination 3 weeks after surgery has central vision increased significantly (VOD 6/9) on the right eye and peripheral vision has partially adjusted on both eyes.
- One-year follow-up outcomes of treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration with aflibercept
- Use of micropulse laser in patients with diabetic macular edema at the department of ophthalmology, university hospital Hradec Králové
- Result of the first 12 months of treatment of macular edema complicating brvo in patients treated with ranibizumab
- Acute myopia with elevation of intraocular tension as an adverse side effect of antidepressant medication
- Change of central and peripheral vision in patient with symptomatic cyst of Rathke's cleft following transsphenoidal resection