Introduction: Orthokeratology lenses present a special type of hard contact lenses, which is used especially for myopic correction. The lenses are applied during the night, when thanks to their special shape cause temporally (reversible) change of the cornea shape. During the day, there is not necessary to wear any other refractive correction. Due to the wearing regimen, there is, comparing to the classical contact lenses, higher risk of health complications. For their safe use, it is necessary to pay attention to the application of lenses of adequate parameters, follow up the care and hygiene precautions, regular controls and early treatment of possible problems. The application of contact lenses should be done by experienced and well-educated expert in contact lens fitting. In the Czech Republic, this method is practically not used.
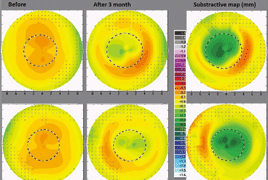
Aim: The aim of the case report was to follow up the course of concrete application of orthokeratology lenses for myopic correction from the optic (refractive) point of view, and to evaluate the optic changes in the system of the eye. In the followed up subject, there were measured subjective changes in refraction, visual acuity, corneal curvature, corneal and whole eye aberrations, and corneal thickness during the period of one month after the beginning of lens application (initial phase). The same parameters were followed-up during one-month period since the termination of lens wearing for three months (second phase). The subject was a woman, 24 years old, myopic, with the refractive error in the right eye –3.0 spherical diopters and astigmatism of –0.25 cylinder in the axis 90°, and in the left eye –2.75 spherical diopters without astigmatism; without ophthalmologic or systemic diseases. The full correction of the refractive error after the orthokeratology lenses application occurred approximately after four nights (wearing the lenses overnight). Concurrently, during the day, slight recurrence to original values was evident. With the decreased refractive error, the uncorrected visual acuity improved accordingly. Further, the flattening of the central cornea was observed, e.g. increasing of the central cornea curvature diameter (maximum change was 0.22 mm in the right and 0.28 mm in the left eye) and slight thinning. The adverse accompanying optic phenomenon was increasing of the aberrations of higher orders, which presented subjectively by decreased visual acuity under mesopic conditions. One month after the termination of contact lenses wearing, all the followed-up parameters returned to original values.
- Clinical Results of Implantation of Two Types of Multifocal Rotationally - Asymmetric Intraocular Lenses
- Hybrid Monovision
- Optical Characteristics of Myopic Corrections by Orthokeratological Contact Lenses
- Bilateral Congenital Multiple Pigment Vitreous Cyst in a Three-Year-Old Girl: Ten Year Observation
- Tattoo-Associated Uveitis
- Magnetic Resonance Strength 1.5T – Possibilities for Optic nerve Imaging