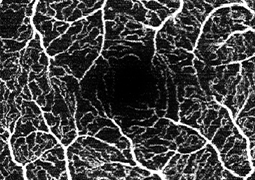
Aim: To evaluate changes in the vascular density of the deep and superficial capillary plexus of the retina, the area of the foveal avascular zone, central retinal thickness, and best corrected visual acuity in patients with diabetic macular edema treated with anti-VEGF agents.
Material and Methods: In a prospective study at the Ophthalmology Clinic of FNHK, we evaluated a group of 41 eyes of 30 patients (19 men and 11 women) with diabetic macular edema treated with Lucentis or Eylea. The average age of the patients was 61.7 ±11.3 years. Average initial visual acuity was 64.4 ±9.1 letters on ETDRS optotypes. During the one-year follow-up period we monitored the density of the deep and superficial retinal capillary plexus using OCTA. We evaluated OCTA scans with the ImageJ program at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months. Additionally, the area of the foveal avascular zone, central retinal thickness, and best-corrected visual acuity were measured.
Results: During the one-year follow-up period there was a statistically significant change in both retinal capillary plexuses, with the density of the deep capillary plexus increasing (p < 0.0001) and the superficial capillary plexus decreasing (p = 0.0073). The area of the foveal avascular zone decreased from an initial average value of 0.29 ±0.14 mm² to 0.24 ± 0.07 mm² (p = 0.0406). Average central retinal thickness decreased from 434.1 ±96.2 µm to 322.2 ±90.8 µm (p = 0.0001). Best corrected visual acuity improved by 7.3 letters on ETDRS optotypes over the year (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Treatment with the aforementioned anti-VEGF agents significantly reduces central retinal thickness and improves visual acuity in patients. It affects the density of the retinal capillary plexuses and the area of the foveal avascular zone. The results of the impact of anti-VEGF agents on macular perfusion vary considerably in the available meta-analyses. The design of the study, the approach to assessing the density of the retinal capillary plexuses, the number and characteristics of patients (including inclusion and exclusion criteria), the duration of the follow-up period, and the specific anti-VEGF agents used are all influential factors.