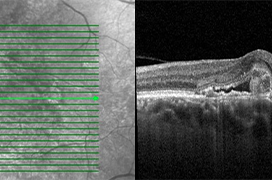
This article presents an overview of treatment regimens of drugs containing antivascular endothelial growth factor for the treatment of neovascular form of age-related macular degeneration. Currently, drugs containing antivascular endothelial growth factor are the only effective treatment for this chronic and progressive disease. The treatment regimens for this disease in the last two decades have seen a shift from a simple endeavor to stabilize the disease to achieving maximum improvement of visual acuity and its maintenance, with improvement of the patient's quality of life and a minimal treatment burden on patients and their families. Other goals of the alternative dosing regimens that have replaced the original fixed regimens were greater individualization of the dosing regimen, better patient cooperation, saving financial costs and reducing the burden on application centers. Age-related macular degeneration, whether dry form or wet form, represents a serious health and socioeconomic problem, as the disease is one of the most common causes of severe and irreversible central visual acuity disorders up to the degree of practical blindness of one or both eyes in people over 50 years of age in developed industrialized countries. The most important issue is to ensure early diagnosis of this disease, followed by prompt and continuous treatment with an individualized proactive treatment regimen, with the aim of stabilizing and improving anatomical and functional results.
- Treatment Regimens of Neovascular Form of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. A Review
- Retinal Vein Occlusion Guidelines
- Screening and Treatment of Retinopathy of Prematurity at The Department of Pediatric Ophthalmology at The Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University and University Hospital Brno
- Comparison of Optical Biometry Data Measured with Lenstar and Anterion Devices
- Evaluation of Optic Disc Drusen Using Modern Imaging Paraclinical Methods
- Refractive Surgery in a Patient with Alport Syndrome. A Case Report